Arteriovenous Malformations (AVM)—A Silent Brain Threat
Center : Neurology Center
Article by : Assist. Prof. Ittichai Sakarunchai

Arteriovenous malformations (AVM) in the brain can cause sudden, severe headaches that have never occurred before, or sudden seizures and limb weakness. These are critical warning signs of a hidden and potentially life-threatening condition in the brain.
Table of Contents
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
- Symptoms of Arteriovenous malformations
- What causes an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
- What are the complications of Arteriovenous Malformations?
- When to see a doctor
- How are Arteriovenous malformations diagnosed?
- How are Arteriovenous malformations treated?
- Can an Arteriovenous malformation be prevented?
- Advanced Arteriovenous malformations Treatment at Nakornthon Hospital
- Free Online Consultation with a Specialist
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
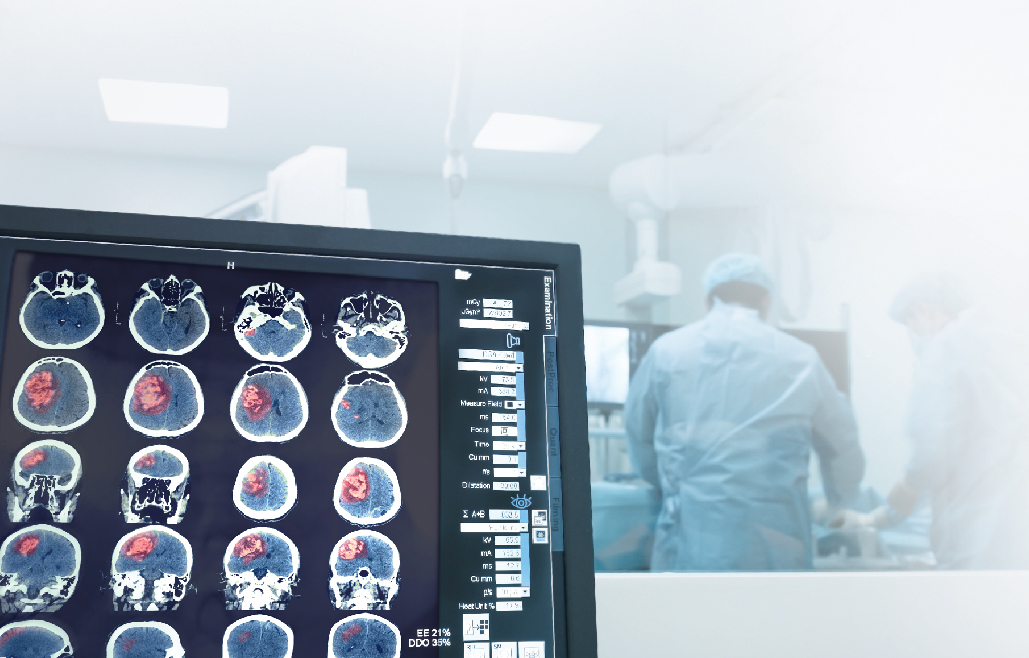
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are congenital abnormalities of the brain's blood vessels, where arteries and veins are connected directly without capillaries to reduce blood pressure. This abnormal connection causes blood to flow at a higher pressure, making the vessel walls fragile and prone to rupture. A rupture AVM can lead to brain bleeding, disability, or even death.
If Arteriovenous malformations are not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications such as intracerebral hemorrhage, which may cause permanent brain damage. AVM is usually present at birth or develops during fetal development. However, most patients show no symptoms during early childhood and often present with symptoms during adolescence or adulthood, typically between ages 10–40.
Symptoms of Arteriovenous malformations


The symptoms of AVM brain conditions vary depending on the location, size, and whether the vascular malformation has ruptured. In some cases, there may be no symptoms until an AVM rupture occurs, causing bleeding in the brain. Possible symptoms include:
- Seizures
- Headache: Chronic or recurring pain in the same area may signal an unruptured AVM. Pain intensity may vary and can resemble migraines.
- Muscle weakness or numbness
- Speech difficulties: Slurred speech, stiff tongue, or trouble understanding language
- Blurred or partial vision loss, double vision, or blindness in one eye
- Unsteady gait or poor coordination
- Confusion, memory loss, or cognitive issues
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Bruit: Some patients may hear a whooshing or pulsating sound in their ear or head due to abnormal blood flow in the av malformation.
What causes an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
An arteriovenous malformation is typically congenital, meaning it develops during fetal growth. Although the exact cause is unknown, it is believed to result from an error during early blood vessel formation. Instead of capillaries, arteries and veins connect directly, leading to abnormal blood pressure levels. In some cases, AVM disease may be hereditary.
What are the complications of Arteriovenous Malformations?
- Brain Hemorrhage (Bleeding): Patients may experience sudden and severe headaches, nausea, or vomiting.
- Pressure on Brain Tissue: Bleeding can compress brain tissue, causing symptoms such as weakness, numbness, facial drooping, slurred speech, vision problems, or even paralysis.
- Seizures: The second most common symptom, especially if the brain AVM is near the brain's surface. Seizures may be partial (involving one body part) or generalized (full-body convulsions, loss of control, unconsciousness).
- Cognitive Impairment: Arteriovenous malformations can affect thinking, memory, reasoning, and decision-making, impacting learning, work, and daily life.

When to see a doctor
Do not ignore symptoms of Arteriovenous malformations like severe headaches, dizziness, vision problems, or changes in cognition. If these symptoms occur—especially if sudden and intense—seek medical attention immediately for timely diagnosis and treatment.
How are Arteriovenous malformations diagnosed?
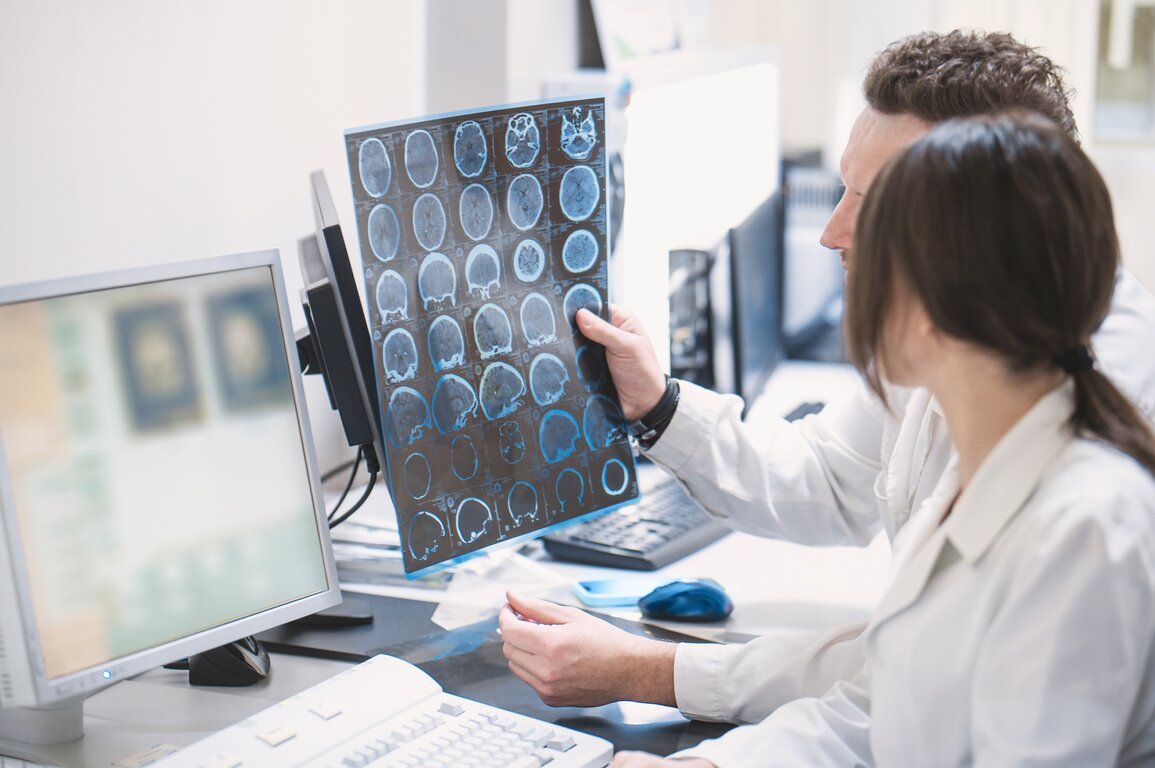

Diagnosing arteriovenous malformation disease involves evaluating its type, location, and severity. Key diagnostic methods include:
- Neurological history and physical examination
- CT Scan: Detects bleeding, swelling, or signs of AVM rupture
- MRI: Visualizes brain tissue and vascular malformation location
- MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography): Assesses blood flow speed and pattern
- DSA (Digital Subtraction Angiography): Provides detailed imaging of abnormal blood vessels, including feeding arteries and draining veins
How are Arteriovenous malformations treated?
Treatment depends on the AVM’s size, location, symptoms, and the patient’s age and overall health. Options include:
- Observation: For small, symptom-free AVMs with very low rupture risk—especially in elderly patients—doctors may monitor with regular imaging.
- Surgical Removal: If located near the surface and at high rupture risk, a neurosurgeon may remove the AVM entirely to prevent future rupture.
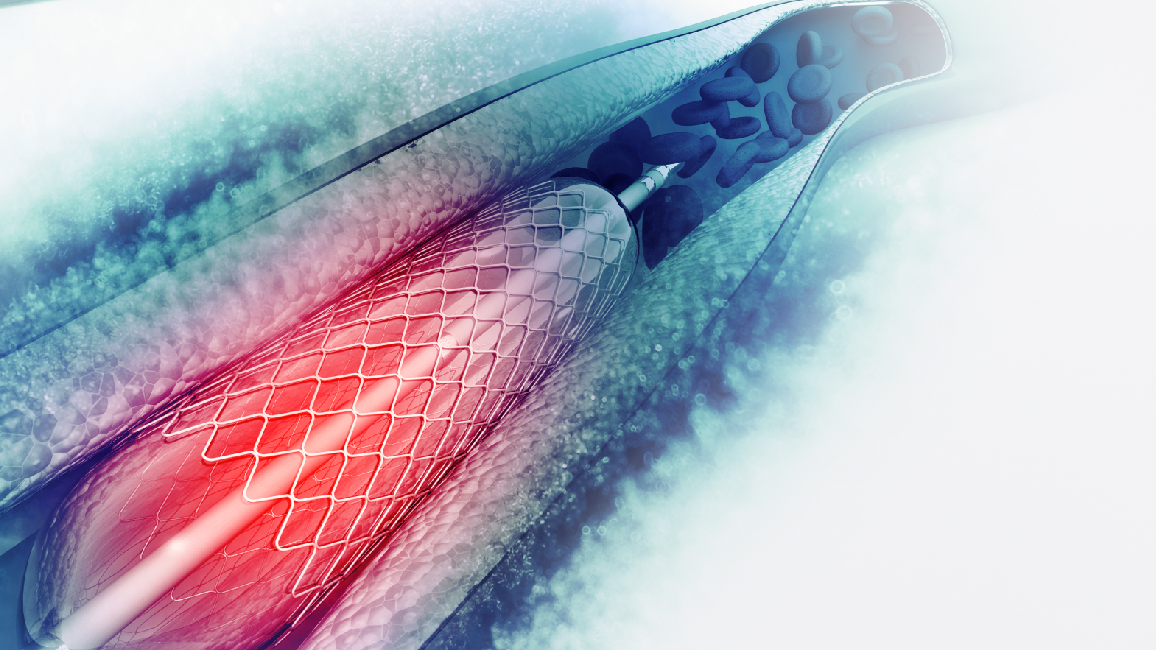
- Endovascular Embolization: A catheter is inserted through the groin or wrist to reach the brain AVM. Special glue or liquid is injected to block blood flow to the AVM.
- Radiation Therapy (Radiosurgery): High-energy beams target the AVM, causing it to shrink over 1–3 years. Ideal for small AVMs (under 3 cm) deep in the brain or near critical areas where surgery is risky.
Can an Arteriovenous malformation be prevented?
Arteriovenous malformations are not preventable as they are congenital and not caused by lifestyle or external factors. However, recognizing symptoms and managing existing AVM brain conditions early can reduce the risk of severe complications like rupture AVM and brain hemorrhage.
Awareness, early diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are key to reducing danger and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Advanced Arteriovenous malformations Treatment at Nakornthon Hospital
If you or a loved one experiences suspicious symptoms or has been diagnosed with Arteriovenous malformations, seeking care from a skilled team with advanced medical technology is essential. The Neurology Center at Nakornthon Hospital offers expert care for AVM disease and also well-prepared to provide care for other brain-related conditions, such as Alzheimer's disease and brain tumors, with experienced neurologists and a multidisciplinary team. The hospital uses advanced diagnostic tools such as biplane DSA for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment planning—ensuring the highest level of care and safety.
For more information, please contact:
- - Website : https://en.nakornthon.com
- - Facebook : Nakornthon Hospital - International Patient
- - Line : @nakornthoninter
- - Tel: 02-450-9999 (Available 24 hours)


Assist. Prof. Ittichai Sakarunchai
Neurological Surgery / Interventional Neuroradiology
Neurology Center
Free Online Consultation
Article of Neurology Center